The age framework of Qarhan Salt Lake in arid western China is still controversial due in part to (1) age discrepancy between conventional 14C and 230Th dating results, and (2) no AMS 14C ages of organic carbon from drilling cores in Qarhan Salt Lake were reported until now. In order to discuss these chronological problems, upper 54.50 m lacustrine sediments from a drilling core (ISL1A) recovered from Qarhan Salt Lake were dated based on 230Th and AMS 14C dating techniques. Results show that (1) AMS 14C ages of total organic carbon (TOC) from 4.65 to 30.29 m are almost in stratigraphic order and consistent with 230Th ages of halite in the corresponding layers; (2) AMS 14C ages of TOC from 30.29 to 54.50 m are younger with increasing depth. This phenomenon was also found in Shell Bar in the study area, suggesting that AMS 14C ages from upper 30.29 m are more reliable while those from lower 24.21 m in ISL1A may be underestimated; (3) 230Th ages of halite from lower 24 m lacustrine sediments are obviously older than AMS 14C ages of TOC in the corresponding layers, which results into different age framework of salt lake sediments in Qarhan Salt Lake; (4) if extrapolating these reliable AMS 14C ages in ISL1A, similar age framework with 230Th ages in this core confirms that 230Th ages are much close to the true ages of these sediments, which suggests that the forming timing of the bottom salt layer is ~50 ka. 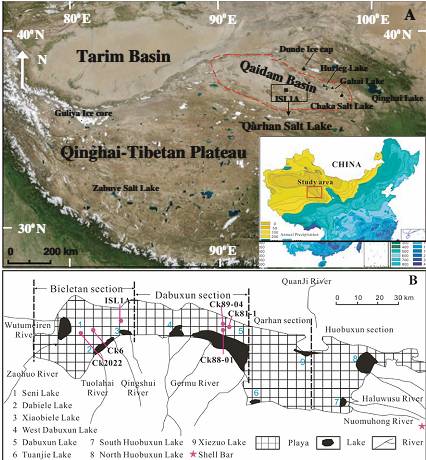
A map showing the location of Qarhan Salt Lake, eastern–central Qaidam Basin and palaeoclimatic recording sites.bMap of drilling cores and salt lakes in Qarhan Salt Lake area. (Photo from the original paper) Original paper link:http://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2Fs12665-013-2526-5.pdf |