China has abundant salt lake resources, rich in lithium, potassium, sodium, magnesium, boron, bromine and other resources. Among them, magnesium reserves reach billions of tons, accounting for more than 70% of the country's magnesium resources. Every 1 ton of potassium or lithium produced will produce hundreds of tons of magnesium by-products. The by-product magnesium salts have low added value and are dumped in large quantities. This not only severely restricts the exploitation of lithium and potassium resources, but also causes the waste of salt lake resources. As the country's requirements for environmental protection increase, as well as the continuous emphasis on comprehensive utilization of resources and balanced mining of mineral resources, the development of magnesium has gradually attracted attention. The preparation of magnesium-based functional materials with high added value is an effective means to realize high-value utilization of magnesium resources and balanced exploitation and comprehensive utilization of salt lake resources.
Magnesium-based hydrotalcite is a type of layered material, which is formed by the accumulation of interlayer anions and positively charged layers. It has the properties of layer metal ion, interlayer guest anion type and quantity adjustable, and material size and shape adjustable. The special structure gives it rich properties and wide applications. As a kind of important magnesium-based functional materials, magnesium-based LDHs and their derivatives have important applications in industrial catalysis, plastics, rubber, biology, environment, textiles and other fields.
The research team of Professor Deng Xiaochuan and Dr. Fan Faying from Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences systematically reviewed the properties, preparation methods and existing problems of magnesium-based hydrotalcite. In addition, its application and characteristics as functional additives of polymer materials, flame retardants, heat stabilizers, ultraviolet shielding agents, adsorbents, catalysts, preservatives, and drug slow-release agents are introduced. The future development direction and application prospects of magnesium-based hydrotalcite are also prospected, which provides a certain reference for the future application of salt lake magnesium resources. For details, please see "Salt Lake Research" Issue 3, 2020-"Research Highlights" of the Special Issue of Salt Lake Chemical Industry: Pages 18-27.
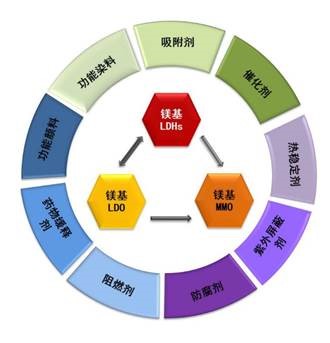
Application of magnesium-based hydrotalcite and its derivatives