China is a large agricultural country. Potash fertilizer has become an important strategic resource for ensuring national food security. With the rapid development of China's economy, the consumption of potash fertilizer also grows rapidly, with an average annual growth rate of around 8.6%. At present, China mainly produces potash fertilizer through the exploitation of Quaternary salt lake brine. Potash fertilizer output can only meet 50%-60% of domestic demand, and potassium salt has long been listed as one of the seven major mineral resources that are in short supply.
The most basic controlling condition of potash mineralization is the three elements of "tectonic-source-climate" in the Earth's supergene environment. The structure is the prerequisite, the source is the necessary condition, and the climate element plays an important role in promoting potassium formation. Based on the above-mentioned coupling relationship of salt formation conditions, foreign scholars have proposed the "Shazhou model", "preparatory basin model" and "abnormal potassium salt evaporite" deposition model. Through investigations of salt lakes and potash resources in China, domestic scholars have proposed the "salt deep basin", "oscillating dehydration in deep alpine basins, separate basin synchrospheric differentiation," "water-bearing walls," and "two-story buildings," etc. mode. These potassium formation models explored the potassium formation laws from the control conditions of evaporite deposits, but there were few studies on the late changes of potash deposition and the spatial patterns of potassium deposits and morphological changes.
The research team of the Salt Lake Geology and Environment Laboratory, through a comprehensive study comparing the deposition of potash salts at home and abroad and the characteristics of late changes, concluded that the potash deposits were determined by basin topography in the early stages of the deposition of potash, and the potash was deposited in the basin water collection center. "Formal salt rock mass depressions; Potassium salt deposition process due to gravity separation caused by the decline of the overlying debris cap, light weight of salt rock and potassium salt uplift, salt rock formation "mouth" form; potash burial late With the squeezing and pushing of tectonic activities, the salt rock and potassium salt further protrude upwards, and the salt rock body presents a "convex" salt anticline. Based on the characteristics of mineral deposits such as potassium and magnesium salt, Lao potassium salt and Spanish potassium salt in Chaerhan Salt Lake in Qinghai Province, the "notch convex" potassium salt metallogenic model was proposed (see below). Changes in evaporite rock deposition shape determine the final occurrence of potassium salt. space. By interpreting the geological and comprehensive geophysical data around the basin, the profile of the salt rock profile in the target area is studied, and the location of the potassium salt burial can be predicted, which is of great significance for the specific potassium seeking work.
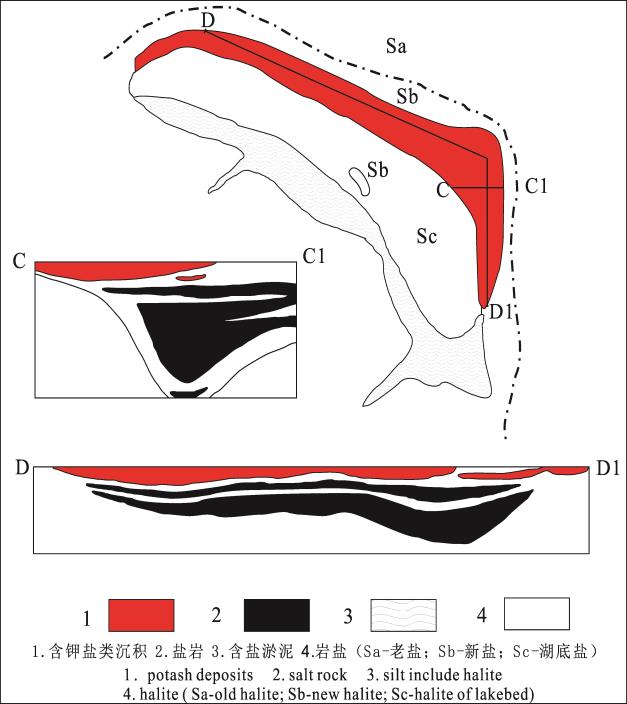
Salt Plane Distribution Pattern and Salt Rock Mass Sediment Profile in Dabson Section of Chaerhan Salt Lake, Qinghai Province
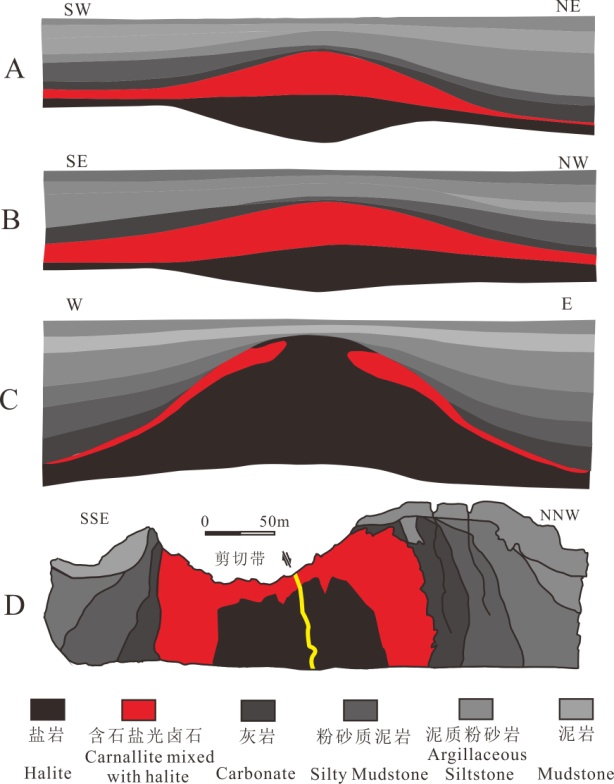
Figure A-B below shows the geological characteristics of the Saitainong knife deposit in Laos,
Figure C-D shows the Panhai Potash Deposit in the Vientiane Basin of Laos and the Catalonian Potassium Deposit in Spain